上週,在美國地球物理學會 (AGU) 秋季會議上,NASA 的 OSIRIS-REx 任務科學團隊展示了他們從小行星貝努獲得的首批發現。正如預期的那樣,該探測器發現了貝努過去存在液態水的證據。“這些發現對我們來說真的非常令人興奮,”任務首席研究員 Dante Lauretta 在新聞釋出會上公佈早期結果時表示。“我們選擇貝努作為目標,正是因為我們認為它含有含水礦物。” Lauretta 和其他團隊成員表示,貝努上的水錶明該小行星還含有富含碳的有機物質,這些物質原始地儲存了太陽系誕生之初的狀態。
貝努是否真的蘊藏著此類有機物還有待觀察。但羥基(與氫和氧鍵合的分子)的發現是該任務科學階段的一個有希望的開始。18 個月後,OSIRIS-REx 將嘗試從貝努表面採集樣本並運回地球,儘管小行星崎嶇不平、環境惡劣的初始影像讓人懷疑這一目標的可實現性。在此之前,該探測器將廣泛繪製小行星地圖,以便找到一個可訪問的取樣點,並揭示這個由比太陽系本身更古老的物質組成的天體的詳細歷史。完成這項工作的主要工具將是兩個 onboard 光譜儀:OTES,用於研究小行星的熱輻射;OVIRS,用於在可見光和紅外光下檢查這塊太空岩石。
飽經風霜的岩石
支援科學新聞報道
如果您喜歡這篇文章,請考慮透過以下方式支援我們屢獲殊榮的新聞報道 訂閱。透過購買訂閱,您正在幫助確保有關塑造我們當今世界的發現和想法的 impactful 故事的未來。
在 AGU 會議前一個月,我正在與 Lauretta 和 OSIRIS-REx 科學團隊的其他成員一起,進行該任務對貝努的首次光譜觀測。當時,關於遠古水的未知證據僅以 0 和 1 的細束存在——一條 1.2 億公里的 tether 連線著 OSIRIS-REx 和 54 號站,後者是馬德里巨型射電天線,是深空網用於行星際通訊的一部分。來自遙遠小行星的資料流將進一步從西班牙傳輸到位於圖森的亞利桑那大學月球與行星實驗室的 Michael J. Drake 大樓。
Drake 大樓以已故的行星科學和 OSIRIS-REx 奠基人之父的名字命名,它樸實無華,隱蔽在圖森北部安靜的住宅區 off-campus。然而,在 2018 年 11 月 5 日的早晨,它很可能成為地球行星科學活動的 epicenter,數十名 frenzied 科學家正在仔細研究剛剛從貝努傳回的新鮮影像。
.gif)
一個動畫展示了 OSIRIS-REx 在前往小行星的最後四個月中看到的貝努景象。最終影像是從約 65 公里的高度獲得的。來源:NASA 戈達德太空飛行中心和亞利桑那大學
在 Lauretta 的辦公室裡,他驚歎於這顆小行星及其 myriad features,外星地質顯示在大型 wall-mounted 螢幕上。從一百公里的高度看,貝努大致呈核桃狀,表面像兩棲動物的皮膚一樣 speckled,光斑和暗斑的 chaotic assemblage,在小行星 rugged terrain 中點綴著 fine-grained 的平滑區域。那裡有盆地和窪地,貝努表面 strewn with boulders。團隊預計會發現一個 order of 10 米的 boulder;但實際上,有數百個。整個上午,OSIRIS-REx 科學團隊的成員 crowded 他的辦公室,參加會議或 informal sneak peeks 剛 unveiled 的遙遠世界。當該任務首次提出時,貝努只是 telescope 中的一個光點,多年來,這就是團隊的 reality。然而,現在,他們看到了一些真實的東西,一些具有 three dimensions 和 personality 的東西——一些比預期的更 grittier 和更 rugged 的東西。這令人興奮。這令人恐懼。
貝努不像龍宮那麼 harsh,龍宮是另一個有 robotic visitor 的小行星——日本探測器隼鳥 2 號將在任務規劃人員確信可以在不 scuttling 在龍宮 unwelcoming surface 上的情況下 retrieve samples 時嘗試 retrieve samples。貝努看起來更年輕;impact craters 很少見。
Lauretta 也是隼鳥 2 號團隊的成員,一項任務的 tribulations inform 另一項任務。他為他的小行星感到驕傲。“從 albedo、color 和 spectral perspective 來看,龍宮 featureless,”他說。“貝努很有趣。” 他說,它的 dark patches 特別有希望。OSIRIS-REx 科學團隊希望在物體上找到 dark, carbonaceous material,因為這種 stuff 可能曾是 planets coagulating from the disk of gas and dust 的 feedstock,而後者是 embryonic 太陽系的 celestial womb。似乎它就在那裡,haphazardly scattered 在小行星表面。darkness 不是陰影;在影像中,太陽幾乎直接位於小行星後面。但這很可能只是 mirage,一種 compositional chimera,由表面 fine grains 對光的 scattering just so 產生。目前尚無人知曉。

Dante Lauretta(center right)於 2018 年 11 月 5 日在圖森亞利桑那大學舉行的“Daily Downlink”會議上與聚集的 OSIRIS-REx 團隊討論了來自貝努的 preliminary data。來源:Heather Roper 和亞利桑那大學
儘管這可能看起來很 tedious,但值得 worry about 貝努表面有多 granular,因為整個任務的 success 可能取決於此。目前尚無 insufficient data 用於 confirmation,但 OSIRIS-REx 團隊曾 predicted 貝努表面將由 centimeter-scale particles dominate。因此,centimeter-scale particles 是其 sample-gathering robotic arm TAGSAM 設計用於 collect 的東西。無法 collect samples 的 sample-collection mission 將令人失望。
時間旅行者
Niels Bohr 曾說過,prediction 很困難,尤其是在預測未來時——或者在這種情況下,當它 concern something no one has ever really seen 時。先前關於貝努成分的一切已知資訊都來自 telescopes,這些 telescopes incapable of spatially resolving 小行星。到目前為止,它充其量就像 looking at 圖森 ridge-ringed horizon 上的 peak。您看到 outline——mountain 存在——但僅此而已。您必須 venture much closer——stand on it,see its rocks、cacti、desert lavenders 和 velvet mesquites。在貝努,OSIRIS-REx 是 humanity 的 proxy mountaineer——其 onboard camera instrument 和 spectrometers 是我們的眼睛,向科學家們 revealing 這個來自 deep time 的 relic 的 true nature。
隨著 data whispers in,1s 和 0s 透過深空網,科學家們可以從 telescopic observation 中說的是:貝努 most closely resembles meteorites called carbonaceous chondrites——特別是 “CI” 或 “CM” varieties。這些是 meteorites,它們在 history 的某個時候與水發生過 interactions。(I 和 M 分別指 Ivuna 和 Mighei——用於建立這些更大的 carbonaceous chondrites groupings 的 individual meteorites 的名稱。carbonaceous chondrites 總共有八個 groups。)
這一切可能看起來並不 important——old rock、ancient water、maybe organics… so what?但在 studying 這個太陽系的 history 時,這些 ingredients 是 everything。Organic material 和 water 對地球上的生命至關重要。但 nobody knows for sure 它們來自哪裡,如何來到這裡的。它們是與我們的太陽形成同時出現的,還是僅在地球及其行星 siblings 形成後才由 comets 和 asteroids 運送而來?貝努及其 brethren hold the answers,因為它們被認為在化學上與我們太陽系的 genesis 保持 unaltered。OSIRIS-REx 今天 studying 的小行星貝努,據信基本上與四十億年前存在的貝努相同。NASA 不是 flying a spacecraft,而是在 flying a time machine,其 purpose 是 figure out 生命的 stuff——bacteria 到 brontosauruses——來自哪裡。
(1).png?w=900)
藝術家 rendering 的 OSIRIS-REx extending 其 TAGSAM sample-collection instrument 到貝努表面。Sample collection 只會在 OSIRIS-REx 在貝努 orbit for more than a year、mapping 表面和 rehearsing carefully choreographed collection process 之後進行。然後,探測器將 store samples 以便最終 return 到地球,將於 2023 年到達。來源:NASA 戈達德太空飛行中心
熱與光
NASA 從未 sampled 過小行星,而且可能在很長一段時間內都不會再次 sample 小行星。rashly grab any old scoop of rock and rocket back home 是不夠的。該機構需要 learn everything humanly and robotically possible about 貝努——需要 understandevery square centimeter of it——以便探測器 samples 的 spot 是 scientifically 最好的 place,可以 answering 關於 under the sun 的一切開端的 so many crucial questions。Long after everyone involved with OSIRIS-REx is dead,taken 的 samples 將 continue to be studied。隨著 humanity 對太陽系的 understanding matures,a little bit of 貝努可以 be revisited endlessly,只需一張 plane ticket 的 price。
“您可以從 orbit 中 learn a lot about a planetary object,”Apollo sample curator 兼 NASA 約翰遜太空中心 Astromaterials Acquisition and Curation Office manager Ryan Zeigler 說,貝努 samples 如果一切順利,應該在 2023 年到達那裡。“當 remote-sensing mission is over 時,however,you’re done。You don’t get any new data。” 他說,Sample-return missions 是 everlasting。“Smart people will one day come along,look at the initial sample science and say ‘That’s great,but we can use those samples to answer questions we didn’t even think about 20 years ago.’ Getting samples in hand on Earth gives you the long-term ability to study a planet in an infinite amount of detail,with massive instruments——some of which haven’t been invented yet。”
因此,sample-site selection 是 generations 之間幾乎 Confucian 的 correspondence。探測器的 instruments work together in service of choosing a worthy sample target,但只有其 spectrometers,OVIRS 和 OTES,可以 answer 關於 composition 的 critical questions。Each is designed to complement and affirm the findings of the other。Pictures reveal extraordinary geologic features,but what,exactly,are they made of?Is this the material we need to bring home and crack open in a laboratory?So important are spectrometers to this interplanetary mission that it is the first-ever to carry not one,but two onboard。
OSIRIS-REx 團隊成員在 2018 年 11 月 5 日舉行的“Daily Downlink”會議上討論了來自探測器對貝努進行 spectrometric reconnaissance 的早期結果。Initial analysis revealed 貝努 to be covered with water-rich hydrated minerals——further evidence it also harbors abundant organic molecules preserved from the dawn of the solar system。來源:Heather Roper 亞利桑那大學
OVIRS measures light from the sun reflected from 貝努。OTES measures thermal energy radiated by 貝努。(The asteroid is like a hot rock on a summer day;put your hand near it and you feel the heat——that emitted heat is what OTES is measuring。)In both cases,the resultant spectral measurements,plotted as waves on graphs,suggest which minerals are present。OVIRS is better with small particles and organic molecules——grimy films,grains of sand and minerals——in large part because the relatively short wavelengths of visible light yield higher resolutions。OTES is better with bigger,bulkier things that can absorb and re-radiate lavish levels of longer-wavelength infrared light——again,think of hot rocks。If OTES sees a certain mineral,OVIRS should see it,too;a disparity between the two can reveal subtleties of particle size and composition useful for diagnosing the true state of things on 貝努’s surface。
The spectrometers are not penetrating deeply into 貝努’s heart;OTES can thermally probe only to a depth about five times the width of a human hair。OVIRS can see only to a single human hair width。During the sampling event in 2022,OTES will be active as the spacecraft approaches 貝努 and presses into it,and will remain in operation as the spacecraft backs away。“Assuming we don’t get dust all over our telescope,we should see what’s underneath that surface,”Southwest Research Institute in Boulder,Colo. 的 Vicky Hamilton 和 OSIRIS-Rex Spectral Analysis Working Group 的 leader 說。“It will tell us something about the uppermost surface of 貝努 and the timescales of change,”she says。“We know asteroid surfaces are space weathered。But is 貝努 space weathered all the way in,which implies particles are constantly moving around,constantly exposing new things to the sun and micrometeorites?Or is it relatively stable,with only the outermost surface seeing the effects?” she notes。This,again,tells scientists something about the goings-on billions of years before there was such a thing as Earth,or Mars,or the sun as we know it。
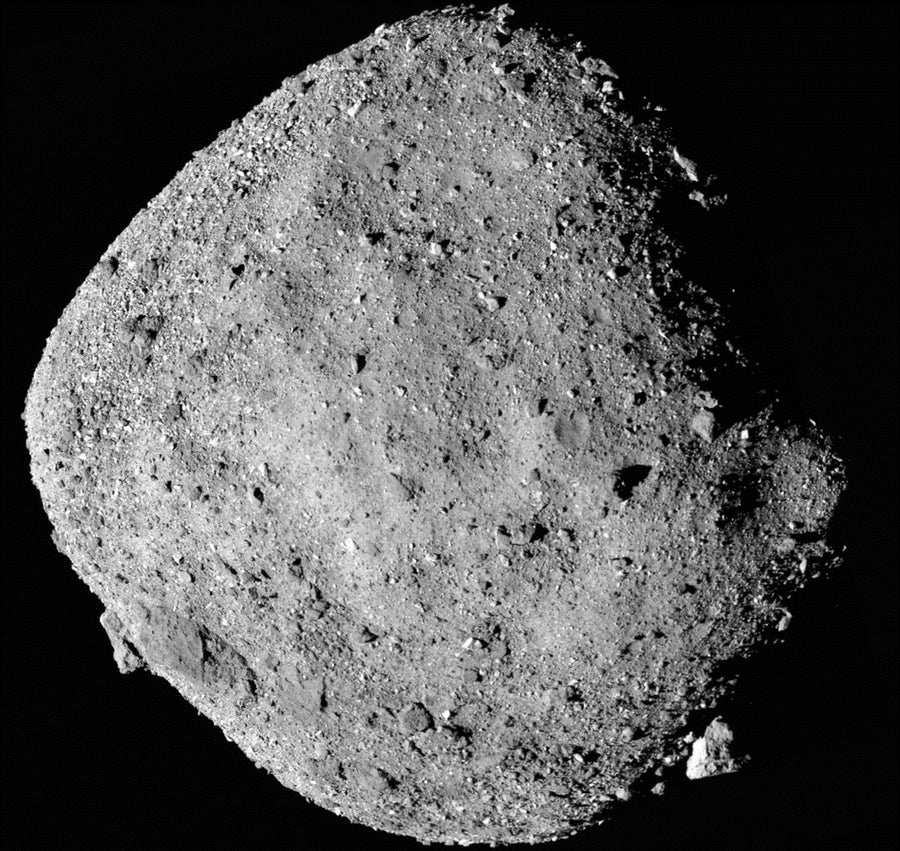

貝努的“full disc”檢視,包含 OSIRIS-REx 的相機從 24 公里高度拍攝的 12 張影像。這顆小行星 boulder-strewn 的表面比預期的更 rugged,complicating OSIRIS-REx 的 sample collection 和 return 的 planning。來源:NASA、戈達德太空飛行中心和亞利桑那大學
抵達
當天下午,隨著 data done trickling 從 heavens 以 light-speed 進入深空網的 dishes,OSIRIS-REx 團隊舉行了 all-hands “Daily Downlink” 會議。11 月 5 日有 43 人出席,不包括來自全國各地的 substantial numbers 的 remote participants virtually participating。
“我知道整棟大樓都在 buzzing,”Lauretta 告訴大家。“我昨晚沒睡好,因為我不得不 keep getting up and looking at the images。” 在一個 standout slide 上,貝努被 rendered 成 Magic-Eye-style,這樣,只需稍微 eye-crossing focus,它就會 suddenly spring into three dimensions。spectroscopy data——line graphs 上的 arcane squiggles——在被 ogled 以揭示任何 beautiful mysteries 之前,還有很長的路要走。No one will ever make spectroscopic Magic Eyes。For now,the signal-to-noise ratio is excruciatingly low。The spectrometers were designed to observe 貝努 from a full field of view,the way the moon might take up the entirety of a backyard telescope’s viewfinder。But because the spacecraft is still so far away,貝努 is filling only about 40 percent of the frame;in addition to the asteroid,the spectrometers are taking readings from deep space。
Even having teased tantalizing results from the data,the month following that first full-frame spectroscopy download involved not “eureka!” moments concerning 貝努’s makeup but rather laborious calibration of the data sets returned。The spectrometers are sensitive:they get too warm and the results are skewed;some voltage is off and the results are skewed;they suffer weathering effects of deep space and the results are skewed。“You don’t want to just run your data blindly and start interpreting science out other end,”Hamilton told me later by phone。Calibration and the blessing of data are aimed,she says,“at making sure nobody,in overexcitement and not knowing everything about how an instrument behaves,goes off and interprets something that is not real。” The instruments are pointing either at 貝努,deep space or,in the case of OTES,an internal calibration target。Known signal variations reveal the state of the instruments。So far,both spectrometers have proved nominal。
12 月 2 日,貝努 at last filled OTES 的 full frame,並且,according to Lauretta,“those data were beautiful。” So far,every spectra taken has revealed hydrated minerals as the team begins the 18-month challenge of assembling a compositional map of every square centimeter of 貝努’s surface in preparation for sample collection in 2020。Hydrated minerals mean 貝努 matches to CI and CM carbonaceous chondrites,which is what the team wanted desperately to get back into laboratories on Earth。It was one relief in advance of a much larger one:The spacecraft’s formal arrival at 貝努 the next day,moving the mission to its operations phase。“I wear a Fitbit,”Lauretta says。“My resting heart rate dropped nine beats per minute when I slept the night after arrival。I didn’t realize how much tension and anxiety I had been carrying。”
But there are still those boulders。No matter how spectacular the spectra or impressive the images,貝努’s unsettling surface terrain presents problems。“We are uncertain that there is a sample-able site right now,”Lauretta says。“We have work to do。I haven’t given up hope。I think we’re going to figure it out。But you never know。There’s still that question mark hanging out there。”
And yet it entices。When OSIRIS-REx presses TAGSAM into 貝努,it will be tilling and taking the soil of a celestial Garden of Eden。The mission itself is practically written in verse;humans dug up the metals and minerals of this world and fashioned a tool to dig up the materials of another。Far into the future scientists will slice into the spacecraft’s quarry and look deeply into our past。And in the spacecraft studying the composition of an asteroid,we see most of all the stuff that humanity is made of。